Running Evals on Large Language Model Responses
Evaluating Large Language Models Used in a Clinical Charting Application
For companies integrating large language models (LLMs) into their applications, a systematic approach to model and prompt evaluation is essential. This allows them to understand the variability in performance and ensures that they are choosing models optimized for their specific use cases.
A Jupyter or Google Colab Notebook offers a straightforward and flexible platform for generating prediction datasets and conducting comprehensive evaluations (evals). As new LLMs are released, these notebooks can be quickly updated and rerun to generate immediate evals on the latest models.
I created a notebook to generate predictions and evaluate the performance of various LLMs for a medical charting app. The “Generate Predictions” section of this notebook contains the process for generating a dataset of predictions from various models under consideration for use in a medical charting application. This section can be easily updated and rerun as new models are released. The “Prediction Evaluations” section contains analysis across several criteria important for this specific use case. This blog post contains just the text and graphical outputs from the “Prediction Evaluations” section. You can view the full notebook here.
Specific Use Case: Medical Charting Application
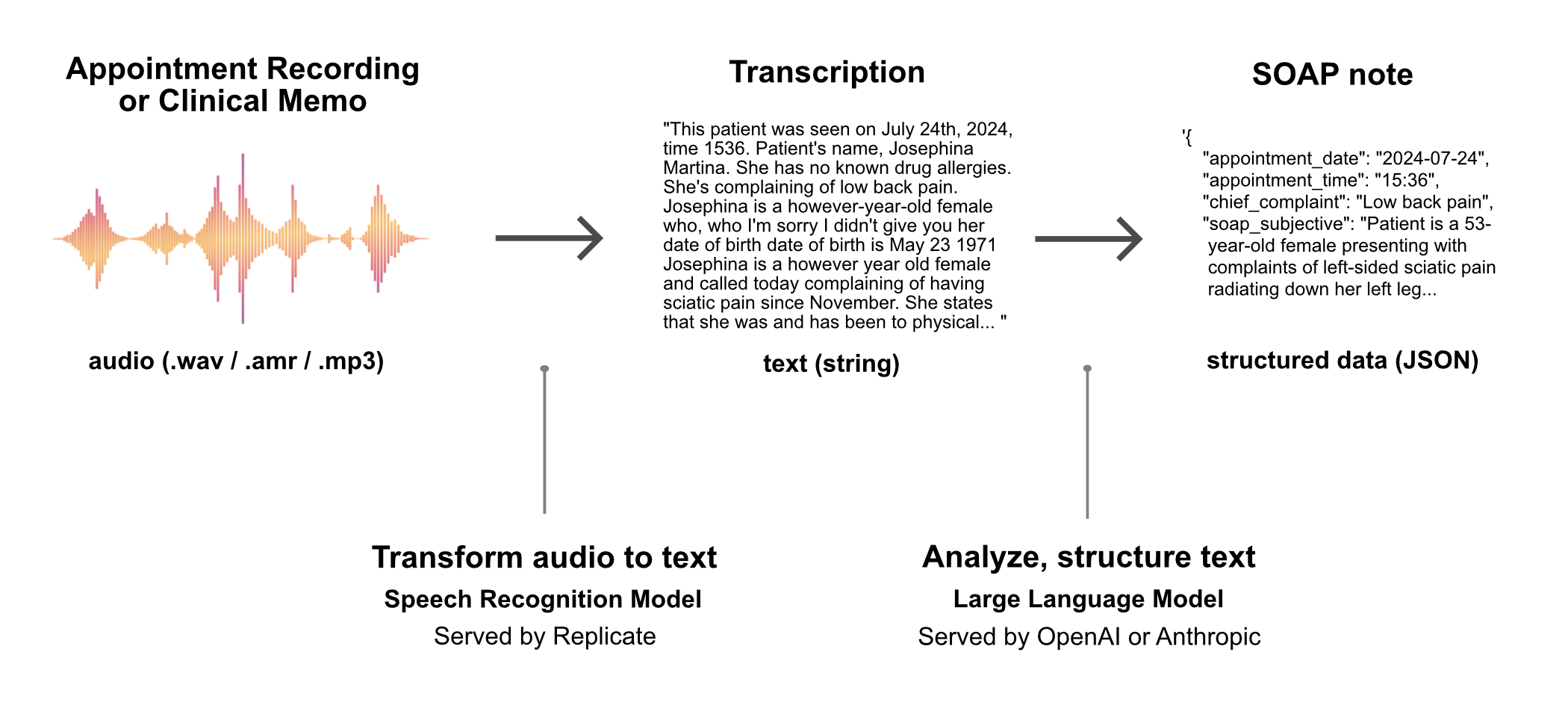
soapnotescribe is a web application that utilizes LLMs to automatically generate structured clinical notes from medical appointment recordings.
The application workflow involves first sending the audio of the medical appointment to a speech-to-text model hosted by Replicate. The transcribed text is then processed by a large language model (served by OpenAI or Anthropic) to organize the content into a structured data object, which is subsequently presented to the physician as a SOAP note. (“SOAP” is an acronym for Subjective, Objective, Assessment, Plan — this is a standard structured format for documenting patient encounters.)
While all major foundational models can generate acceptable SOAP notes from audio transcriptions, they differ significantly in completion times, costs, and quality. Simple pass/fail evaluations are not sufficient to grasp the performance differences of different models under consideration.
The objective of this notebook is to systematically evaluate the performance of models available to convert transcriptions into structured SOAP notes and determine whether the application should be updated with one of the newly released models from OpenAI.
Assessing New Models from OpenAI
Before this analysis, I had been using gpt-4o-mini in production with completely satisfactory results. With the release of the gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18 and gpt-4o-2024-08-06 models from OpenAI, I updated the first section of this notebook and reran the evaluations to determine what kinds of improvements, if any, were offered by these models. These systematic evals provided clarity on the following:
- The performance difference between gpt-4o-mini and gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18.
- The performance difference between gpt-4o and gpt-4o-2024-08-06.
- Whether it would be beneficial to switch from gpt-4o-mini to gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18 or gpt-4o-2024-08-06.
Prediction Evaluations
In addition to standard evaluations such as cost, response time, and prediction length, this notebook contains evaluations that are specific to this particular use case and scoped down to individual fields in the requested JSON schema:
- Length of differential diagnosis field.
- Inclusion of alternative treatment plan in differential diagnosis.
- Correction of medication spelling errors from transcript.
- Correction of medication formatting errors from transcript.
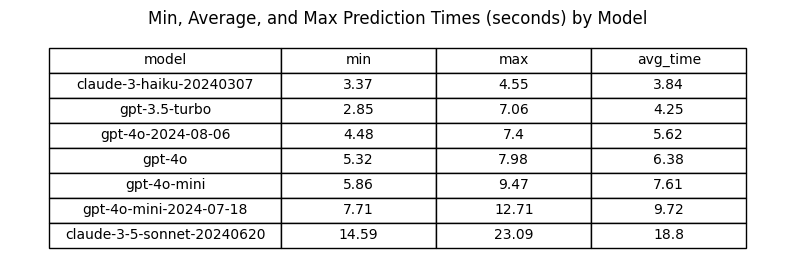
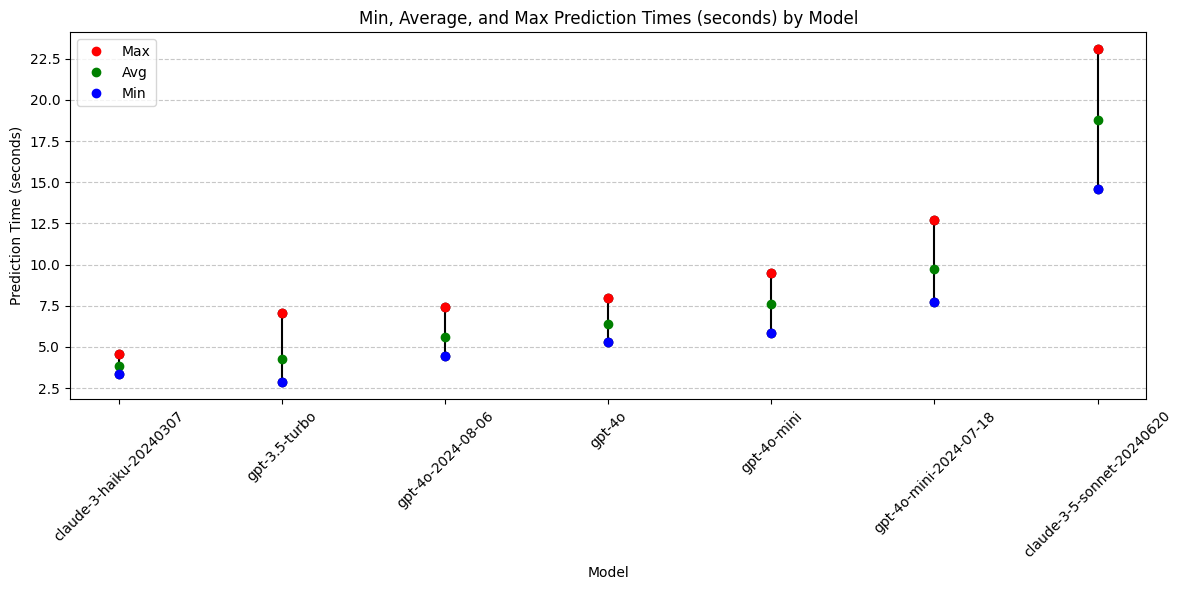
Analysis: Prediction Time
How long does it take for each model to return a response? Note that for some applications the variability of response times may be an important consideration. This dataset shows that some models are much more consistent in their response times than others.
Performance difference between gpt-4o and gpt-4o-2024-08-06
gpt-4o-2024-08-06 avg prediction time: 5.62 seconds
gpt-4o avg prediction time: 6.38 seconds
Absolute difference: -0.77 seconds
Relative difference: -12.01%
Performance difference between gpt-4o-mini and gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18
gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18 avg prediction time: 9.72 seconds
gpt-4o-mini avg prediction time: 7.61 seconds
Absolute difference: 2.11 seconds
Relative difference: 27.72%
Conclusions: Prediction Time
-
gpt-4o-2024-08-06 predictions take about 0.77 seconds (12%) less time on average than gpt-4o predictions.
-
gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18 predictions take about 2.1 seconds (28%) longer on average than gpt-4o-mini predictions
-
Prediction time is not the most important criteria for this use-case, but getting predictions in under ten seconds is desirable. For this reason, switching from gpt-4o-mini to gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18 does not look advantageous.
Models With Best Prediction Speed and Consistency:
- claude-3-haiku (reliably under 5 seconds)
- gpt-3.5-turbo
- gpt-4o-2024-08-06
Analysis: Prediction Cost
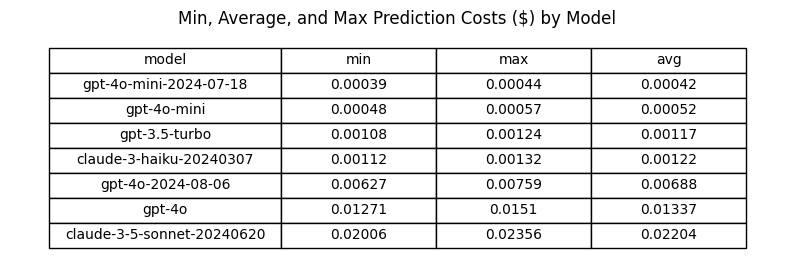
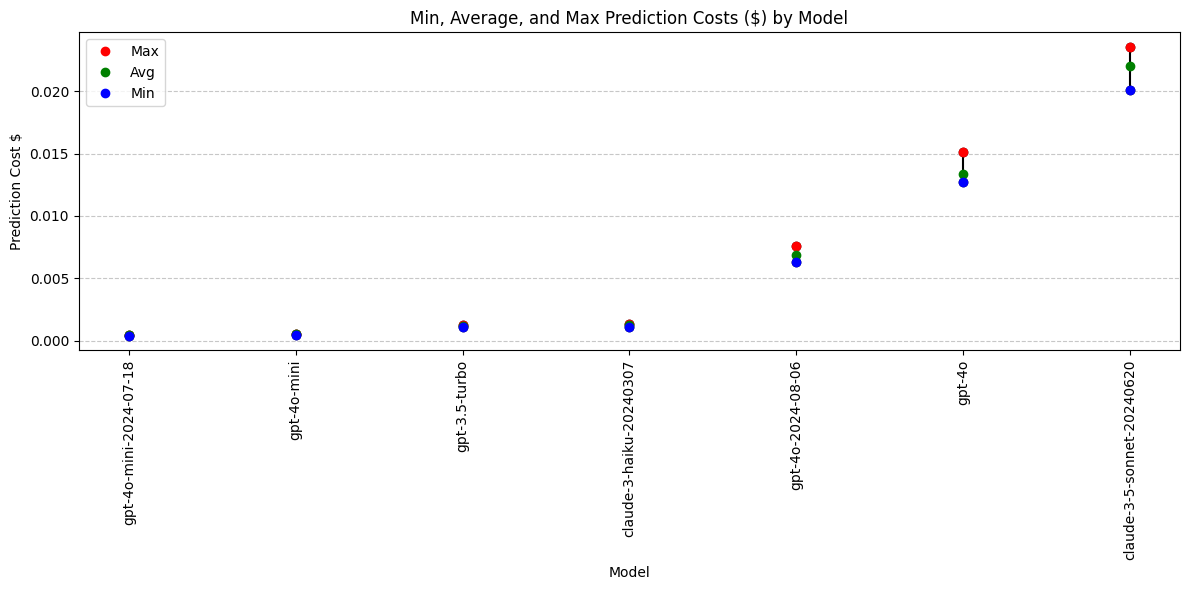
Performance difference between gpt-4o and gpt-4o-2024-08-06
gpt-4o-2024-08-06 avg prediction cost: $0.00688
gpt-4o avg prediction cost: $0.01337
Absolute difference: -0.00648
Relative difference: -48.51%
Performance difference between gpt-4o-mini and gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18
gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18 avg prediction cost: $0.00042
gpt-4o-mini avg prediction cost: $0.00052
Absolute difference: -0.00011
Relative difference: -20.37%
Conclusions: Prediction Cost
- gpt-4o-2024-08-06 has a 48.5% lower average prediction cost compared to gpt-4o.
- gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18 has a 20.4% lower average prediction cost compared to gpt-4o-mini.
- gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18 is now the least expensive model.
Models With Best (Lowest) Cost:
- gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18
- gpt-4o-mini
Analysis: Output Tokens
Which models are more or less verbose?
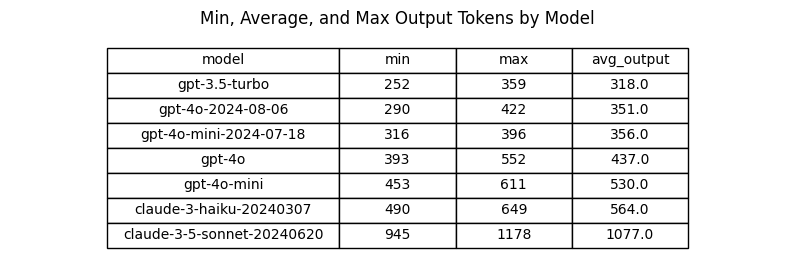
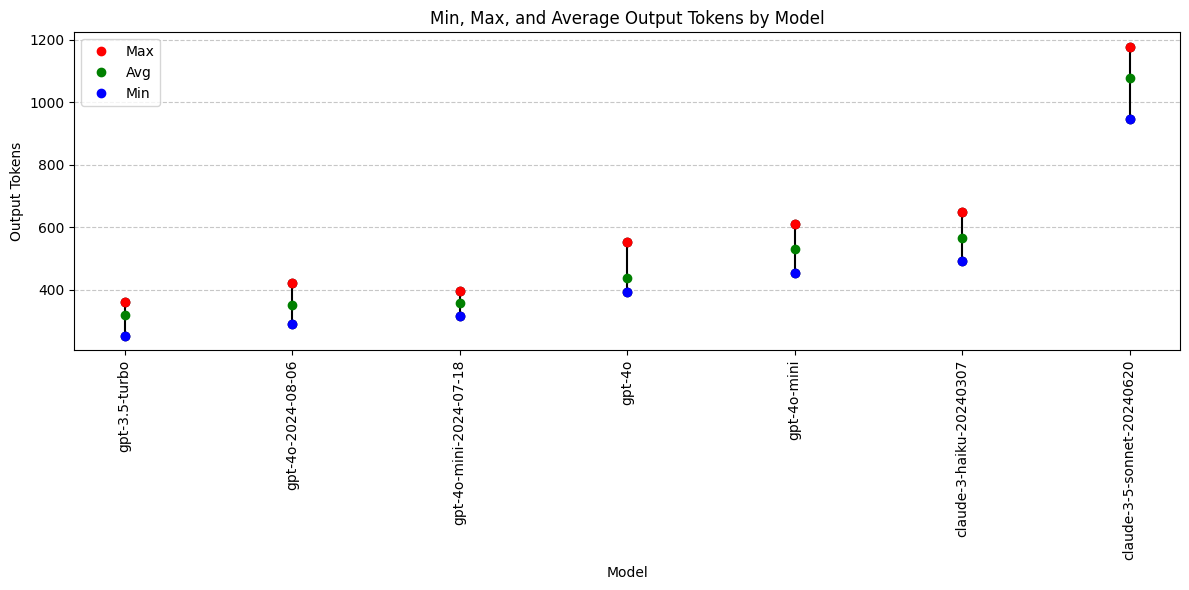
Performance difference between gpt-4o and gpt-4o-2024-08-06
gpt-4o-2024-08-06 avg output tokens: 351.40 tokens
gpt-4o avg output tokens: 436.90 tokens
Absolute difference: -85.50 tokens
Relative difference: -19.57%
Performance difference between gpt-4o-mini and gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18
gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18 avg output tokens: 356.30 tokens
gpt-4o-mini avg output tokens: 529.90 tokens
Absolute difference: -173.60 tokens
Relative difference: -32.76%
Conclusions: Output Tokens
- The new models from OpenAI appear to be less verbose than their counterpart models.
- gpt-4o-2024-08-06 returns about 20% less tokens than gpt-4o
- gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18 returns about 33% less tokens than gpt-4o-mini
- This less verbose behavior may not be advantageous. Brevity is not necessarily preferred for this use case.
- Anthropic’s Claude models generally produce more verbose outputs compared to OpenAI’s GPT models.
- claude-3-5-sonnet is an outlier in output token length.
Models With Best Output Token Length:
- Not applicable. Longer/shorter is not necessarily better.
Analysis: Differential Diagnosis
- Was a Differential Diagnosis returned? If so, what was the average length?
- How many Differential Diagnosis values included “alternative treatments” as requested in the system prompt?
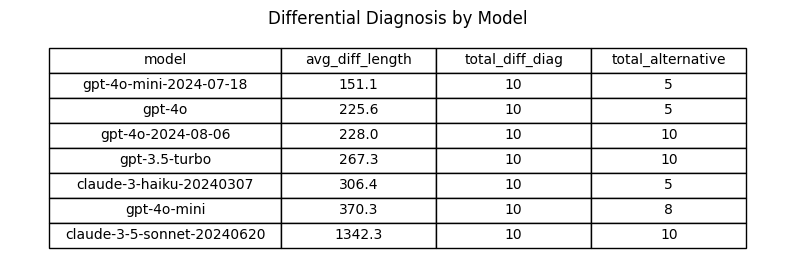
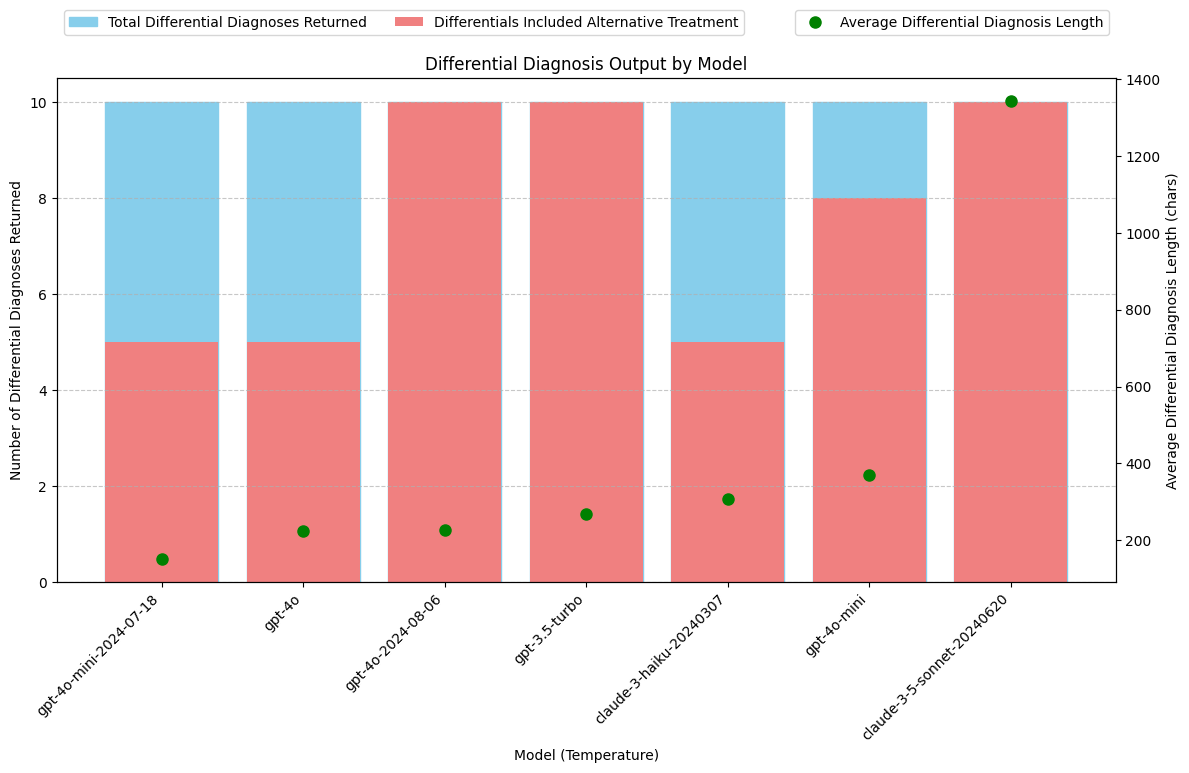
Performance difference between gpt-4o and gpt-4o-2024-08-06
gpt-4o-2024-08-06 avg length of differential diagnosis: 228.00 chars
gpt-4o avg length of differential diagnosis: 225.60 chars
Absolute difference: 2.40 chars
Relative difference: 1.06%
Performance difference between gpt-4o-mini and gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18
gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18 avg length of differential diagnosis: 151.10 chars
gpt-4o-mini avg length of differential diagnosis: 370.30 chars
Absolute difference: -219.20 chars
Relative difference: -59.20%
Conclusions: Differential Diagnosis
The claude-3-5-sonnet model is an outlier with Differential Diagnosis outputs that are 3 to 5 times longer than those of other models. Manual review indicates that these longer outputs are of high quality and significantly enrich the SOAP notes.
gpt-4o-2024-08-06
- gpt-4o-2024-08-06 returns a differrential about the same length as gpt-4o
- gpt-4o-2024-08-06 returns an alternative treatment plan 100% of the time; compared to gpt-4o which only returned an alternative treatment plan 50% of the time.
gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18
- gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18 returns a differrential about half the length as gpt-4o-mini
- This less verbose behavior may not be advantageous. Brevity is not nessesarily preferred for this use case.
- gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18 returns an alternative treatment plan 50% of the time; compared to gpt-4o-mini which returned an alternative treatment plan 80% of the time.
Models With Best Differential Diagnosis:
- Claude-3.5-Sonnet: Consistently provides a detailed Differential Diagnosis along with alternative treatment options, as requested. Notably produces longer, more comprehensive responses.
- gpt-3.5-turbo: Reliably returns a Differential Diagnosis with alternative treatment options.
- gpt-4o-2024-08-06: Reliably returns a Differential Diagnosis with alternative treatment options.
Analysis: Fixing Transcription Errors
The transcript includes the text “Vicodin 5-3, 25 milligrams” for when the speaker said “Vicodin five slash three twenty-five milligrams.” This should have been transcribed as “Vicodin 5/325 milligrams.”
The dosage of medications is typically written with a slash (”/”) to clearly separate the amounts of each ingredient. “5” represents the amount of hydrocodone (usually in milligrams), and “325” represents the amount of acetaminophen (also in milligrams). “Vicodin 5/325” means each tablet contains 5 mg of hydrocodone and 325 mg of acetaminophen.
The transcript also includes a spelling error related to a medication name: “flexor all 20 milligram tablets” should be “Flexeril 20 milligram tablets”.
While this was not specifically requested in the prompt, some of the models caught these mistakes in the transcript and automatically fixed them in the response.
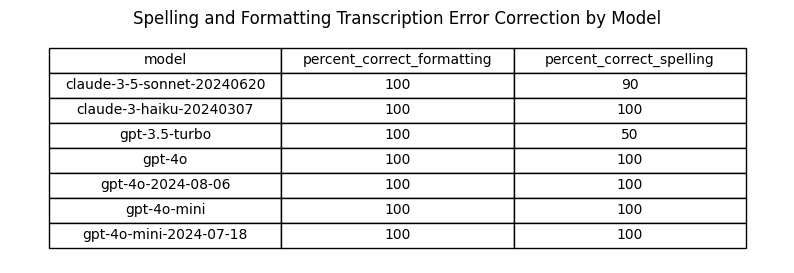
Conclusions: Fixing Transcription Errors
- All models reliably fix the medication formatting error in the transcript.
- Except for claude-3-5-sonnet and gpt-3.5-turbo, all models are catching the spelling errors 100% of the time.
- Manual inspection of claude-3-5-sonnet and gpt-3.5-turbo predictions that did not catch spelling errors reveals unexpected behavior:
- On the one occasion when claude-3-5-sonnet failed to correct the spelling of “flexor all” for “Flexeril,” the model actually made the correction to “Cyclobenzaprine,” which is the generic name for Flexeril.
- On the five occasions when GPT-3.5-turbo failed to correct the spelling of “flexor all,” the model actually omitted the medication from the note entirely. This error is far more concerning.
Model Comparisons
gpt-4o-2024-08-06 compared to gpt-4o
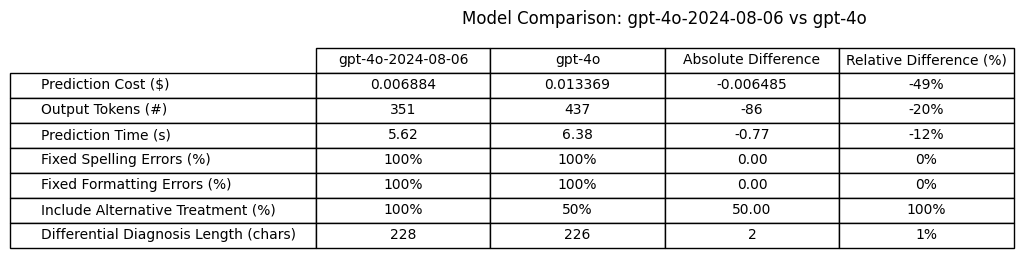
Output Tokens: Less verbose (20% less output tokens)
Cost: Better (49% cost reduction due to price cut and output reduction)
Prediction times: Better (0.77 seconds shorter / 12% shorter avg time)
Fix Transcription Spelling Errors: Equal
Fix Transcription Formatting Errors: Equal
Include Alternative Treatment Plan with Differential: Better (100% success rate compared to 50%)
Length of Differential Diagnosis: Equal
Conclusion: gpt-4o-2024-08-06 is better than gpt-4o for this use case
gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18 compared to gpt-4o-mini
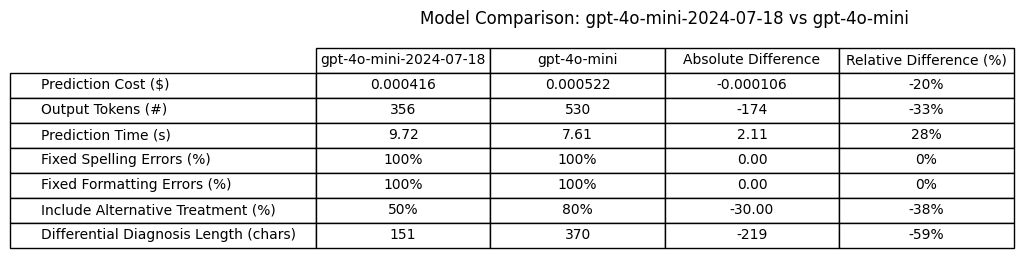
Output Tokens: Less verbose (33% less output tokens)
Cost: Better (20% cost reduction simply due to output reduction)
Prediction times: Worse (2.11 seconds longer / 27.7% longer avg time)
Fix Transcription Spelling Errors: Equal
Fix Transcription Formatting Errors: Equal
Include Alternative Treatment Plan with Differential: Worse (50% success rate compared to 80%)
Length of Differential Diagnosis: Less verbose (59% shorter)
Conclusion: gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18 is worse than gpt-4o-mini for this use case
Overall Model Rankings by Criteria
Lowest cost:
- gpt-4o-mini
- claude-3-haiku
- gpt-3.5-turbo
Inclusion of Alternative Treatment with Differential Diagnosis:
- claude-3.5-sonnet (long, very thorough)
- gpt-3.5-turbo
- gpt-4o-2024-08-06
- No other models scored 100%
Fixing transcription errors:
- All models 100% except claude-3.5-sonnet and gpt-3.5-turbo
Quick, consistent prediction times:
- claude-3-haiku (reliably under 5 seconds)
- gpt-3.5-turbo
- gpt-4o-2024-08-06
Takeaways:
- gpt-4o-2024-08-06 is generally an improvement over gpt-4o. Perform more detailed analysis on output token reduction and what information might be dropped due to less verbose behavior.
- gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18 is not a significant improvement over gpt-4o-mini for this use case.
- Consider Switching Model to gpt-4o-2024-08-06:
- 100% reliability for including alternative treatment plan
- Faster response time
- More expensive model, but cost difference has reduced
Determine Implications of Switching to gpt-4o-2024-08-06 from gpt-4o-mini
Compare model now under consideration (gpt-4o-2024-08-06) to model currently used in production (gpt-4o-mini) to understand implications of switching models.
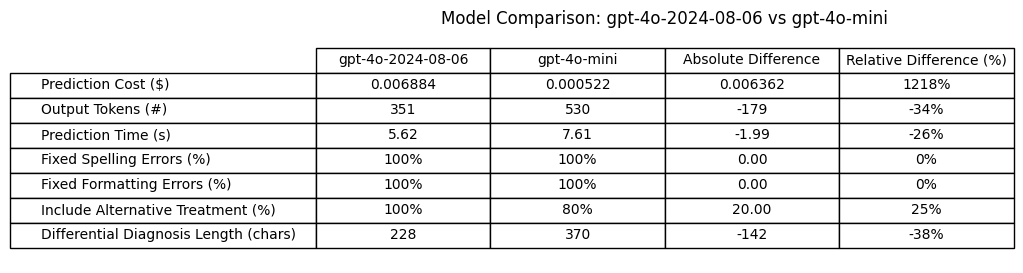
Implications of switching to gpt-4o-2024-08-06 from gpt-4o-mini:
Cost: Worse (12 x the cost of gpt-4o-mini)
Output Tokens: Less verbose (34% less output tokens)
Prediction times: Better (2 seconds shorter / 26% shorter avg time)
Fix Transcription Spelling Errors: Equal
Fix Transcription Formatting Errors: Equal
Include Alternative Treatment Plan with Differential: Better (100% success rate compared to 80%)
Length of Differential Diagnosis: Less verbose (38% shorter)
Conclusion:
- If getting 100% inclusion of alternative treatment plans in the differential diagnosis and quicker response times would make a significant improvement for users of this application, gpt-4o-2024-08-06 could be a better model than gpt-4o-mini for this use case. However, while response time may be specific to that model, it may be possible to get an alternative treatment included in the differential by further developing the prompt.
- Test separating alternative treatment plan into a separate required field on the JSON Schema to force a 100% successful inclusion rate from gpt-4o-mini.
- Note that switching over to gpt-4o-2024-08-06 from gpt-4o-mini will have a 12x increase on prediction costs.
Recommendations:
- Perform detailed review on differential diagnosis results from gpt-4o-2024-08-06 and gpt-4o-mini to understand what information, if any, is being left out in less verbose responses.
